Cat Eye Colors Exposed: 8 Types and Their Extraordinary Rarity
Discover the world of rare cat eye colors. Unlike many other domestic animals, domestic cats boast a stunning array of eye colors. While certain hues may be associated with particular breeds, others can be found among both purebred and mixed-breed felines.
The Rarity of Different Eye Colors
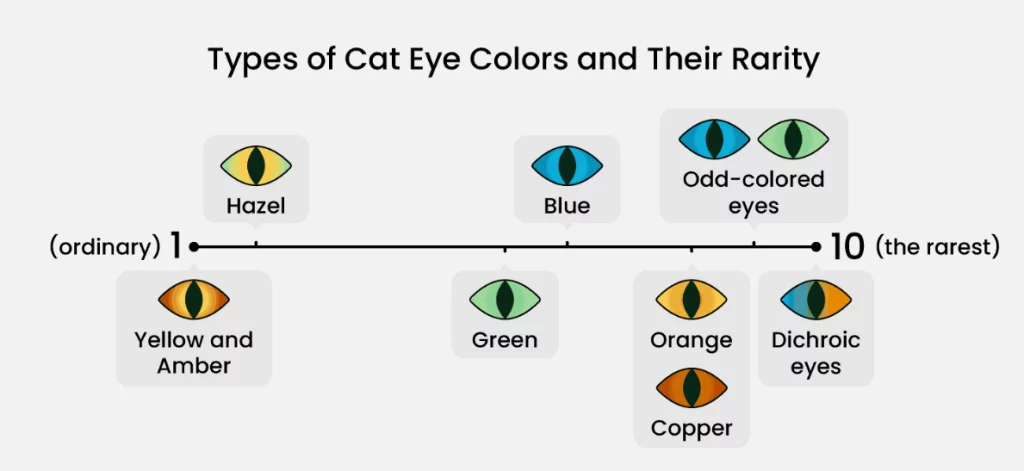
Exploring the Spectrum of Cat Eye Colors: Discovering Eight Common Hues and Their Rarity Ratings on a Scale of 1-10!
These colors don’t adhere to strict boundaries, making it challenging to precisely categorize your cat’s eye color into a single shade. Your cat might possess an eye color that falls somewhere between two hues. It’s more accurate to perceive cat eye colors as a continuous spectrum of shades that seamlessly transition rather than distinct, separate categories.
The 8 Cat Eye Colors
1: Dichroic Eyes
Dichroic, or dichromatic, eyes in cats exhibit a mesmerizing combination of two distinct colors within each eye, a phenomenon that is both stunning and exceptionally rare. This enchanting effect arises from variations in melanin levels in specific regions of their irises.
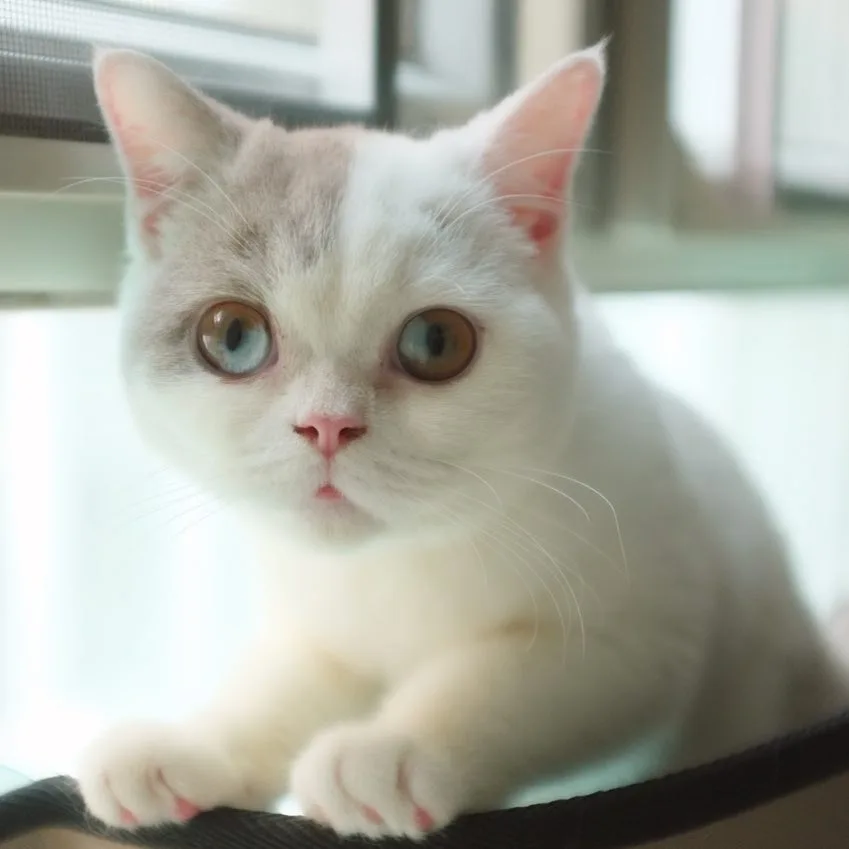

In some cases, you may observe a distinct oval of one color closer to the pupil, seamlessly transitioning into another color. Alternatively, the colors may be divided into sections, with one quarter or half of the eye displaying one hue while the remaining section showcases a different one. There are also instances where one eye possesses a solid color while the other eye remains dichroic.
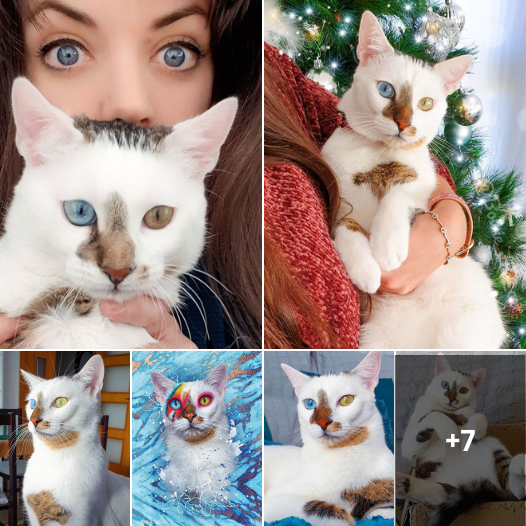
2: Odd-colored Eyes
Have you ever seen a cat with odd-colored eyes?
The scientific term for eyes of different colors is ‘heterochromia iridium,’ where each iris displays a distinct hue. Heterochromia can be a result of inheritance, a congenital condition, or may occur due to accidents or injuries. This unique eye condition is frequently observed in white cats carrying the epistatic gene. Typically, one eye appears blue while the other takes on shades like green, hazel, yellow, or even orange.
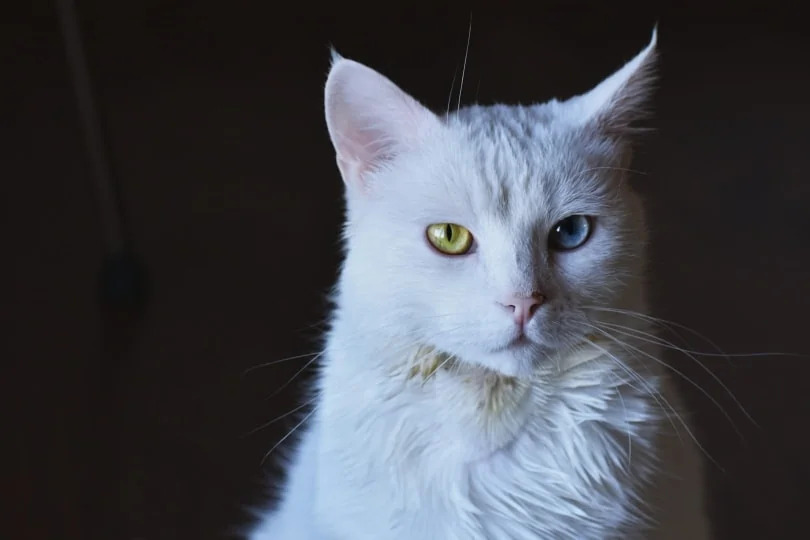

Heterochromia is notably common in specific cat breeds, such as the Turkish Van, Japanese Bobtail, Persian, and Sphynx.
3: Copper Eyed Cats
Copper represents one of the most intense and deepest eye colors seen in cats. These eyes tend to be a rich, light brown shade with hints of red and orange undertones. Occasionally, you may notice tiny flecks of yellow, green, or even more intense shades of orange within this captivating hue. Copper eyes are relatively rare, distinguishing themselves from typical orange eyes while maintaining their unique and unusual charm.

Notably, the Japanese Bobtail, Maine Coon, Persian, Cornish Rex, and Chartreux breeds are known to sport these striking copper-colored eyes.
4: Orange Eyed Cats
While distinguishing between a green eye with yellow flecks and a yellow eye with hints of green may pose a challenge, identifying orange cat eyes is unmistakable. The inception of this vibrant eye color can be attributed to British cat breeders who aimed to create an eye color that would distinctly contrast with any coat color.

Several breeds, such as the Devon Rex, Japanese Bobtail, American Wirehair, Maine Coon, and Turkish Van, are known to exhibit captivating orange eyes.
5: Yellow and Amber Eyed Cats
Yellow eyes encompass a spectrum, spanning from soft lemony hues to dazzling shades of gold, eventually culminating in deep and opulent ambers.
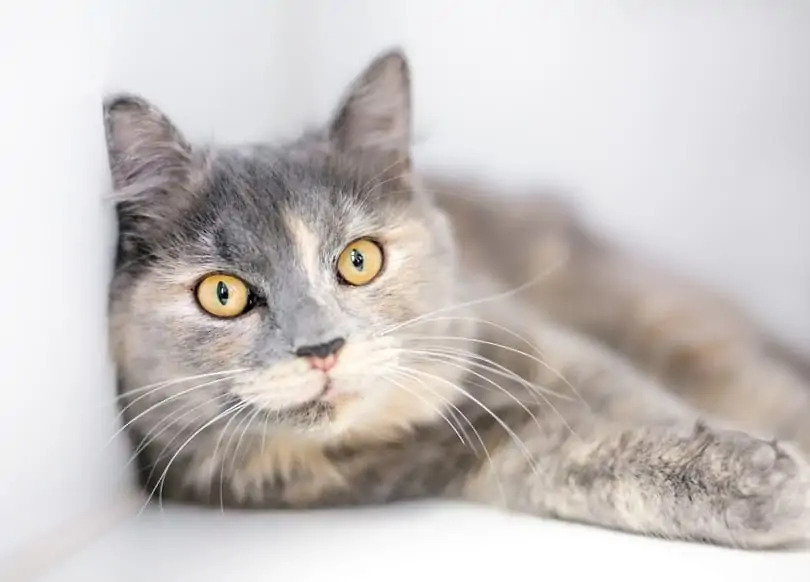

Among the breeds known for sporting yellow or amber eyes are the Bengal, American Shorthair, Manx, British Shorthair, LaPerm, Bombay, Sphynx, and the Norwegian Forest Cat.
The Burmese cat breed, in particular, stands out with its remarkably striking golden eyes, where show cats often boast shades of remarkable brilliance and depth.
6: Hazel Eyed Cats

Hazel eyes are a captivating fusion of both green and golden yellow hues. This eye color is commonly found in wild cats inhabiting temperate regions, such as Lynx and Bobcats, and it’s also a prevalent choice among feral cats. Among domestic cat breeds, those with hazel eyes include the Abyssinian, Bengal, Singapura, Cornish Rex, and Scottish Fold.
7: Green Eyed Cats
The spectrum of green cat eyes encompasses a range, from those with green tinged with yellow undertones, to pure and vibrant green, and even a combination of green with hints of blue. Occasionally, one may notice delicate flecks of gold or yellow scattered within the iris of a green-eyed cat.
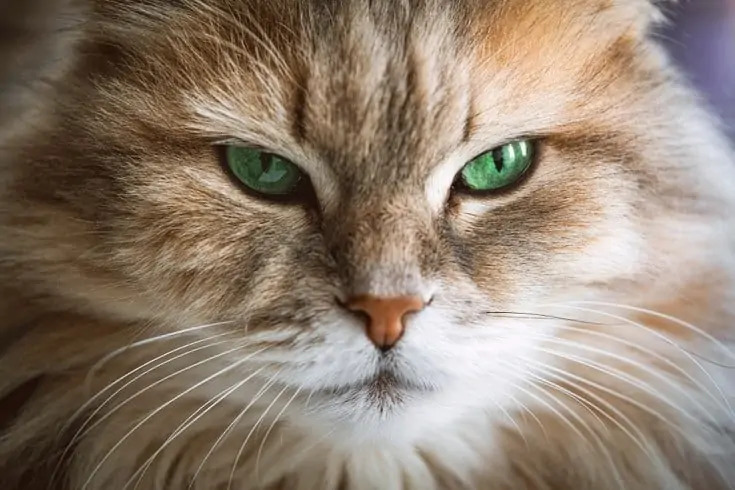

You can spot green eyes in various breeds. For instance, the Egyptian Mau boasts bright gooseberry green eyes, Havana cats exhibit captivating emerald green eyes, and Norwegian Forest Cats come in different shades of green eyes. Additionally, the Russian Blue cat breed is known for its striking and vivid green eyes.
8: Blue Eyed Cats
Blue cat eyes are captivating and unique, devoid of melanin in their irises. These eyes appear clear, with the blue color arising from the way light reflects within the curved contours of the iris. It may sound extraordinary, but it’s a fascinating truth. Blue eyes can span a spectrum, ranging from a delicate sky blue to a deep and dazzling sapphire.

Blue eyes are notably more prevalent in white cats, largely due to the influence of the dominant white gene known as the epistatic white gene. This dominant gene effectively masks other genes responsible for coat color, resulting in a completely white fur. However, white cats with blue eyes, influenced by this dominant gene, are at a higher risk of being deaf compared to their counterparts with green or yellow eyes. The gene responsible for a white coat and blue eyes can lead to rapid degeneration of the cochlea in a cat’s inner ear shortly after birth.
Several breeds are renowned for their striking blue eyes, including the well-known Siamese and Ragdoll breeds. Additionally, other cat breeds, such as the American Shorthair, British Shorthair, Balinese, Persian, Maine Coon, and Devon Rex, can also exhibit captivating blue eyes.
The color of a cat’s eyes is influenced by melanin.
The color of a cat’s eyes is determined by a complex interplay of genetic factors. This is why siblings from the same parents can have different eye colors. Key factors influencing a cat’s eye color include the refraction of light, iris pigmentation, and genetic inheritance.
The iris, the visible part of the eye, consists of two layers. The inner layer contains specialized pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. The depth and richness of the eye color are contingent on the amount of melanin, the natural pigment produced by these cells.
A higher melanin content in a cat’s iris results in darker eye colors, which can span from lemon yellow to hazel, deep orange, or brown. Another contributing factor is the stroma, the outer layer of the iris, which is typically clear but can vary from nearly colorless shades of blue to deep blues and even violets.
When a cat has blue-colored eyes, it’s because they lack any pigment; the blue hue arises from the way light is refracted by the stroma.

All kittens are born with cloudy blue eyes. Around the age of 6 weeks, their eye color may begin to change, revealing their eventual eye color. This transformation occurs based on the presence of melanocytes and the production of melanin. By the time a cat reaches 12 weeks of age, their definitive eye color will have fully developed.






